What Is The Hormone Oxytocin ?
What is the hormone oxytocin?
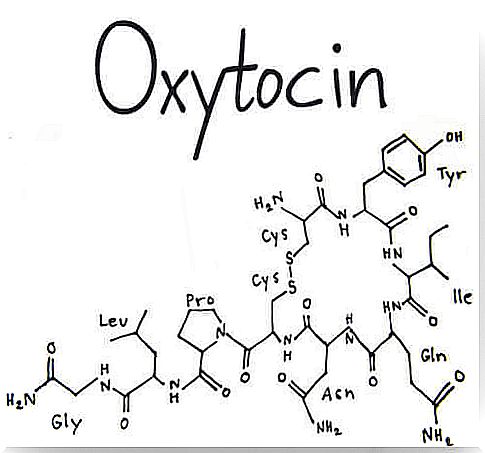
Oxytocin is known for inducing labor and the role it plays in breastfeeding. It consists of 9 amino acids, including:
- cysteine
- tyrosine
- isoleucine
- glycine
- proline
- asparagine
It is located in the posterior pituitary gland and is highly involved in various physiological processes.
Its chemical composition is similar to the hormone vasopressin, which is located in the anterior pituitary gland and has several functions.
As with any organic substance, oxytocin has several receptors. These are mainly found in the:
- womb
- Kidneys
- Bones
- Heart
- Brain
- Ovarian Tissue
- mammary gland
Oxytocin mainly has functional characteristics that have made it the pregnancy hormone. This is because of the effect on different processes on a physiological level.
What does oxytocin regulate?
Reproduction
First of all, this hormone has a clear function in the female reproductive system. One is that it induces labour. It also increases its speed.
Normally , the body releases large amounts of oxytocin as labor progresses. In addition, the levels are even higher if there is nipple stimulation of the woman in labor. High oxytocin levels generate contractions of the uterine muscle wall (myometrium). This facilitates the birth of the fetus.
On the other hand, this hormone acts directly on the erectile tissue, in both the corpus cavernosum and corpus spongiosum of the male reproductive system. Thus, this hormone is also associated with ejaculation through the ejaculatory tract and the urethra.
mammary gland
The hormone oxytocin also induces contractions in the myoepithelial cells of the mammary gland. Thus , it is involved in milk production through the Montgomery glands. In general, this facilitates the breastfeeding process during areola stimulation by the newborn.
Kidney system

Urinary retention caused by this hormone is closely related to molecular events in the basolateral ducts of the kidney.
This decreased production of urine with symptomatic hyponatremia is most often seen in pregnant women who have been induced with oxytocin during labor.
Birth
By nature, oxytocin receptors in the uterus during labor are directly dependent on the levels of this hormone in the body. In the early stages of labour, the best starting dose is between 1 to 6 mU/min. After that, it increases every 15 to 60 minutes.
From that moment on, the receptors will have a greater hormonal bond with oxytocin. Thus, it improves contractions to facilitate delivery.
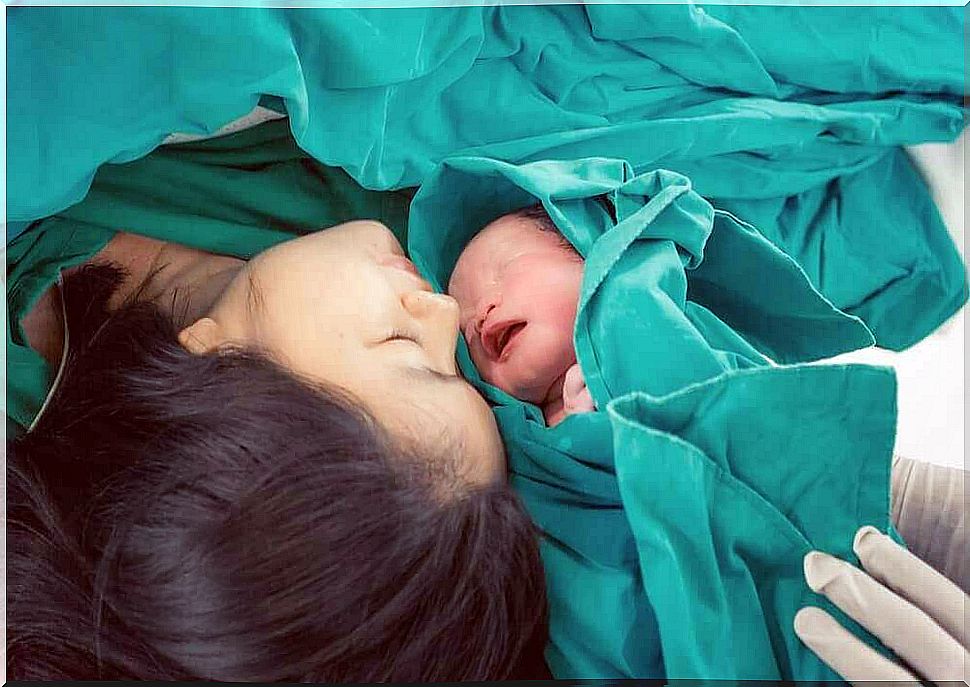
Mother-child relationship
By nature, the mother-child relationship begins immediately after birth. Believe it or not, both the natural and artificial composition of oxytocin takes care of this.
In general, the hormone strengthens the mother-child relationship. An interesting fact is that the same substance makes women forget the pain of childbirth. Because of this, they will not be afraid to have more children in the future.
Hormone side effects

Like all synthetic hormones , oxytocin is not harmless and can cause adverse effects during administration. For example, think of:
- Arterial hypertension
- Abrupt mood swings
- Tachycardia in mother and fetus
- Abnormal postpartum cramps
The side effects associated with moderate to high levels of oxytocin in the body have been noted in patients receiving it. But despite these side effects, it does facilitate contractions during labour.