Agranulocytosis: Symptoms And Treatments
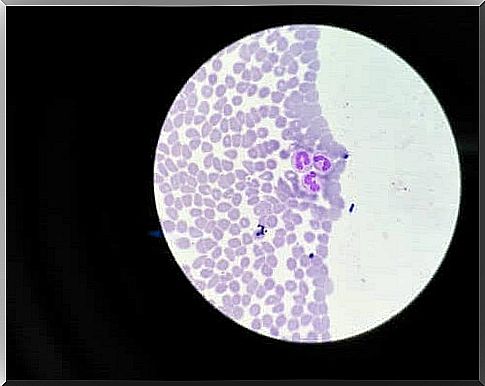
Agranulocytosis is a blood disease that develops when there is a decrease in granulocytes in the blood. Granulocytes are a type of cells in our blood and are primarily responsible for fighting infection. Agranulocytosis is also known as neutropenia or granulocytopenia.
By the most common definition, it occurs when the number of neutrophils (type of white blood cells) is less than 1000-1500 cells per cubic milliliter of blood. There are three types of granulocytes:
- neutrophils
- eosinophils
- basophils
It is a rare but potentially serious disease. In this article you will learn what this disease entails, what the possible symptoms are and what options there are for treatment.
Why does agranulocytosis occur?
As you read above, agranulocytosis is a disease that occurs when the number of neurophiles in the blood decreases. This can happen for the following different reasons:
- Ineffective granulopoiesis: An error has occurred during the neurophile-making process, which takes place in the medulla. As a result, any spinal condition can cause this. For example, it can occur as a result of aplastic anemia or leukemia.
- Premature destruction or consumption of neutrophils: If this happens faster than the spinal cord can generate new neutrophils, agranulocytosis can develop.
Neutrophils are the cells responsible for fighting bacterial infections. As a result, they will work overtime in these situations.
In addition , premature destruction can occur as a result of the ingestion of certain medications, such as metamizole. This can also happen as a result of radiation or autoimmune processes.
The possible causes of agranulocytosis can be divided into three groups:
- Genetic: When the production of the cells is altered by a problem in the genes.
- Congenital: In some cases, you can be born with this disease.
- Acquired: Agranulocytosis can be caused by drugs or due to cancer.
The classification of agranulocytosis
The severity of agranulocytosis is classified according to the number of neurophiles in the blood. The different classifications are:
- Mild: The number of neurophiles is less than 1000-1500 cells per cubic milliliter of blood.
- Moderate: The number of neurophiles is less than 500-1000 cells per cubic milliliter of blood.
- Severe: The number of neurophiles is less than 500 cells per cubic milliliter of blood.
Symptoms
This disease often has no specific symptoms. It can even go unnoticed. However, some of the most common symptoms include:
- Fever higher than 38º C, usually accompanied by chills and sweats.
- Coughing and shortness of breath.
- Weakness and fatigue.
- Mouth sores and sores on the legs.
- Discomfort when urinating.
- Vomiting and diarrhea.
In addition, there may be a change in the vaginal discharge in women. The most important thing to know is that the patient suffers from infections more often. There are also often very unusual or rare infections.
Diagnosis
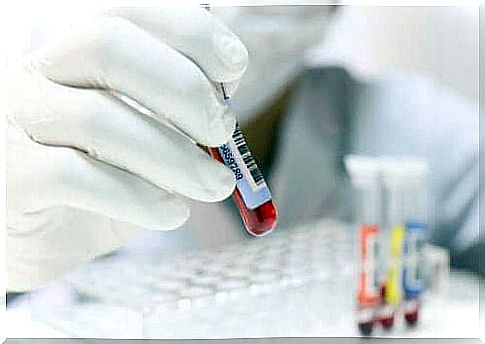
Doctors may suspect this disease if the patient often suffers from infections. First, the doctor will order a blood test, which will show a low granulocyte count if the patient has this disease. The bone marrow can also be examined by means of bone marrow biopsy and/or a biopsy.
Other tests that serve to make the diagnosis include:
- Analysis of urine or other body fluids: In this way, infectious agents can be found if the patient has a fever.
- Genetic testing.
- Determining the antibodies: These tests are good to rule out an autoimmune disease.
Treatment of agranulocytosis
Treatment depends on the cause and severity of the disease. Thus, if the cause is pharmacological, the patient should immediately stop taking the drug that causes it.
If this is not possible, one should ideally try to replace the drug with another drug. Doctors should also order control blood tests.
In case of infection, the patient should take antibiotics. The most common strategy is to take antibiotics against the most common microorganisms. When agranulocytosis is due to an autoimmune disease, corticosteroids can lead to good results.
There are also more specific treatments available today, such as:
- Leukocyte transfusion.
- Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factors (G-CSF). This is a method in which the bone marrow is stimulated to produce more granulocytes. This treatment is especially effective in people whose agranulocytosis is the result of chemotherapy.
- Bone marrow transplant: This method is only used for cases where other treatments have not worked. Healthy bone marrow can produce healthy granulocytes. However, it is difficult to find a suitable donor.
Conclusion
Agranulocytosis is a complex blood disease. It is necessary to consult a doctor if you often suffer from infections and you suspect that you have this disease. You should also see your doctor if you feel weak and have a fever or other symptoms. The doctor will conduct the appropriate examinations and prescribe the necessary treatment.